The world of food and drink can be difficult to navigate for those of us with dietary restrictions, but fortunately, there are plenty of options to suit every lifestyle. Lactose intolerance affects millions of people around the world, and it can be difficult to know which foods you can enjoy without feeling uncomfortable.
Kefir is a fermented milk product that has become increasingly popular in recent years, but can people with lactose intolerance enjoy it too?
Kefir is a rich source of probiotics, vitamins and minerals, making it a great choice for health-conscious people. It is made by adding kefir grains to milk or non-dairy milk and letting the mixture ferment for up to 24 hours. During this process, the natural bacteria found in kefir grains break down much of the lactose found in milk, reducing it to levels acceptable to most people with lactose intolerance.
Although people with more severe forms of the condition may still have difficulty digesting kefir, even after fermentation, it is generally safe for people with milder forms. However, it should be noted that although kefir contains lower levels of lactose, it still contains a certain amount of lactose. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to your body’s reaction to this product.
If you experience any symptoms of lactose intolerance, such as bloating, nausea or diarrhea, it’s best to avoid kefir and find another way to get your probiotics.
The good news is that other dairy products, such as yogurt, cheese and butter, contain much lower levels of lactose, which may make them suitable for people with this condition. For most people with lactose intolerance, kefir can be a comforting, nutrient-dense food that still fits into their diet.
Remember to be aware of your body’s reactions and always talk to your doctor before adding new foods or drinks to your diet.
More about lactose intolerance
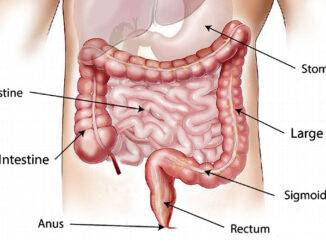
Lactose intolerance is a condition in which the body is unable to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Lactose intolerance occurs when the small intestine does not produce enough of the enzyme lactase, which is needed to break down lactose into glucose and galactose for absorption into the bloodstream.
There are a few different causes of lactose intolerance. The most common cause is primary lactase deficiency, which occurs when the body naturally produces less lactase as a person ages. This type of lactose intolerance is most common in adults and can be inherited.
Secondary lactase deficiency can also cause lactose intolerance. This occurs when the small intestine is damaged due to a disease or injury, and as a result, the body is unable to produce enough lactase.
Another less common cause of lactose intolerance is congenital lactase deficiency, which is a genetic disorder that causes a complete absence of lactase from birth.
Lactose intolerance can cause symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, gas, diarrhea, and nausea after consuming dairy products. While there is no cure for lactose intolerance, there are dietary changes and lactase supplements that can help manage symptoms.
How much lactose does Kefir contain?
The lactose content in milk kefir can vary depending on the fermentation time and conditions as well as the type of milk used to make it. In general, kefir milk contains less lactose than regular milk because the lactose is broken down during fermentation by the beneficial bacteria and yeast present in the kefir grains.
Studies have shown that the lactose content of milk kefir can vary from about 0.2% to 3%, depending on the type of milk used and fermentation conditions. For example, a study published in the Journal of Dairy Science found that kefir made from whole cow’s milk has a lactose content of about 2%, while kefir made from skim milk has a lower lactose content, about 0.2%.
It should be noted that although kefir milk contains less lactose than regular milk, it may still contain enough lactose to cause symptoms in some people with lactose intolerance. If you’re lactose intolerant and are considering trying milk kefir, it’s best to start with a small amount and monitor your symptoms to see how you tolerate it.
What affects the lactose content of milk Kefir?
Several factors can affect the lactose content of milk kefir, including:
- Fermentation time: The longer the fermentation time, the lower the lactose content of milk kefir. This is because the beneficial bacteria and yeast in the kefir grains continue to break down the lactose into glucose and galactose during fermentation.
- Temperature: The lactose content of milk kefir may be affected by the temperature at which it is fermented. Higher temperatures can result in more rapid fermentation and lower lactose content, while lower temperatures may slow down fermentation and result in higher lactose content.
- Type of milk: The lactose content of milk kefir can vary depending on the type of milk used to make it. For example, kefir made from cow’s milk may have a higher lactose content than kefir made from goat’s milk or sheep’s milk.
- The strains of kefir grains: The type of kefir grains used to ferment the milk can also affect the lactose content of milk kefir. Different strains of kefir grains may have varying abilities to break down lactose during fermentation.
Overall, it’s important to keep in mind that while milk kefir is generally lower in lactose than regular milk, it may still contain enough lactose to cause symptoms in some people with lactose intolerance. If you’re lactose intolerant and considering trying milk kefir, it’s best to start with a small amount and monitor your symptoms to see how you tolerate it.
Possible side effects of Kefir for people with lactose intolerance
Although Kefir contains considerably less lactose than natural milk, it still contains some lactose, and people with lactose intolerance may face some side effects after using Kefir.
The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the individual’s level of lactose intolerance and the amount of kefir consumed.
Some possible side effects of kefir for people with lactose intolerance include:
- Bloating: Lactose that is not digested by the small intestine can pass through to the large intestine, where it can be fermented by bacteria, producing gas and causing bloating.
- Abdominal pain: Lactose that is not absorbed by the small intestine can also cause abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Diarrhea: In some people with lactose intolerance, undigested lactose can cause diarrhea.
- Nausea: Consuming kefir may also cause nausea in some people with lactose intolerance.
- Skin rash: In rare cases, people with lactose intolerance may develop a skin rash after consuming kefir.
It’s therefore best to start with a small amount of kefir and monitor your symptoms to see how you tolerate it. If you experience any adverse effects, it’s best to avoid kefir or consider lactose-free alternatives.